Table of Contents
About Diabetes
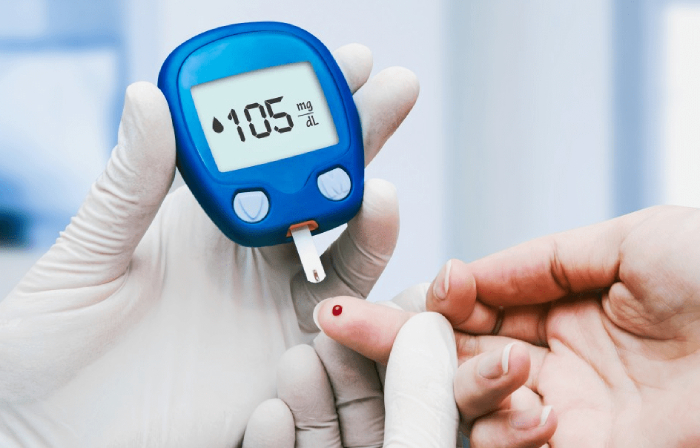
Diabetes mellitus is when the body produces insufficient insulin or does not usually respond to insulin, resulting in abnormally high blood sugar (glucose) levels.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is becoming a speedy and prevalent problem. In Singapore, 105 percent of the population had diabetes in 2010. Disease is a condition in which blood glucose or sugar control is impaired. Long-term uncontrolled high blood glucose levels can lead to multiple complications. The food we eat is digested and converted into “glucose” in our bodies. Glucose is a simple form of sugar that gives energy to the body to carry out necessary activities and cells. Too much or too little glucose is not good. A feedback system maintains the ideal glucose level in our body, which is where insulin comes into play.
What Is Insulin?
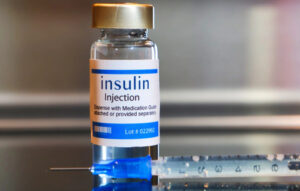
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas. When our body senses that food is in the form of. Controlling blood glucose levels is essential. Glucose, insulin is released from the pancreas. Insulin forms glucose in the blood and is taken into the cells, which are used as energy to carry out normal body functions. Insulin helps the body clear excess glucose from the blood after each meal and keeps the blood glucose in the normal range. However, when there is a problem with insulin production or function, blood glucose levels are out of control, commonly known as diabetes.
Also Read: Chrissy Metz’s Weight Loss Journey: Shedding 100 Pounds
Types Of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
The body’s immune system attacks the insulin producing cells of the pancreas in type 1 diabetes, and more than 90% of them are permanently destroyed. As a result, the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Type 1 affects only 5 to 10% of people with diabetes. Type 1 strikes most people before 30, though it can strike later in life.
Scientists believe that an environmental factor perhaps a viral infection in childhood or adolescence or a nutritional factor causes the immune system to destroy the pancreas’s insulin-producing cells. Some people are more vulnerable to environmental factors due to a genetic predisposition.
Also Read: 6 Things To Consider Before Choosing A Microblading Service
Type 2 Diabetes
In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas often produces insulin, sometimes at higher than normal levels, especially early in the disease. However, as the body develops resistance to insulin’s effects, insulin is insufficient to meet the body’s needs. As type 2 diabetes progresses, the ability of the pancreas to produce insulin decreases.
Type 2 diabetes was once rare in children and adolescents, but it has become more common. However, it usually begins in people over 30 and becomes progressively more common with age. 26% of people over the age of 65 have type 2 . People of specific racial and ethnic backgrounds have a higher risk of developing type 2: Blacks, Asian Americans, American Indians, and Spanish or Latin American ancestry living in the United States have two to three times the risk compared to whites. Type 2 is also inherited.
Obesity is a significant risk factor for developing type 2 , and 80 to 90% of people are overweight or obese. Because obesity causes insulin resistance, obese people require more significant amounts of insulin to maintain normal blood glucose levels.
Chronic Complications Of Diabetes
Diabetes-related complications become more likely when is not well controlled. High blood glucose levels increase harmful substances in the body. They affect small vessels as well as medium and large vessels. Minor vessel problems can affect organs such as the eyes, kidneys, and feet. Diabetic eye disease is retinopathy and can lead to vision loss and blindness if left untreated or undiagnosed. A diabetic kidney initially shows protein in the urine, leading to kidney failure and dialysis. Finally, abnormal foot sensation can lead to diabetic foot complications such as ulcers and infections. Along with these medium and large vessel problems are diabetic foot conditions such as coronary heart disease, stroke, and gangrene.
Also Read: Beyond the Canvas: Unveiling Trendsetting Tattoo Ideas for Men
To Prevent Long-Term Complications Of Diabetes
Make sure your diabetes is under control, and check your blood pressure and cholesterol levels. And quit smoking. It is also essential to undergo appropriate screening at your disease clinic every year to detect these problems.
Symptoms Of Diabetes
- Very thirsty
- dry mouth
- Need to urinate frequently
- Feeling tired and lethargic
- Increased appetite
- blurred vision
- Slow healing of wounds
- Groin itching
- nausea
12 Super Foods To Control Diabetes
1. Lettuce
2. Cinnamon
3. Broccoli
4. Eggs
5. Fatty fish
6. Straderry
7. Garlic
8. Turmeric
9. Extra virgin love oil
10. Nuts
11. Bitter gourd
12. Chia seeds
Infographic: Diabetes: Types,Complications,Prevent& Symptoms